Set up Foreman and manage it with Ansible
Table of Content
- Table of Content
- Introduction
- Setting up the Foreman server
- Install and configure the ansible server
- Managing Foreman - Your first playbook
Introduction
Managing Foreman recently and got bored to configure it each time I set it up from scratch.
This blog post will cover initial foreman install on a CentOS 7 server and then manage it with ansible through the foreman ansible collections.
The repository used in this article is locate here.
Server recommendations
Minimum Foreman server hardware recommendations to support CentOS 7 & 8.
- CentOS 7
- 4 CPUs
- 8Gb RAM
- 100 Gb HDD
Minimum ansible server recommendations:
- CentOS 7
- 1 CPU
- 256 Mb RAM
- 8 Gb HDD
Setting up the Foreman server
Configure the OS
Create a CentOS 7 server with the above hardware setting and make sure to have a working DNS for that server or edit its own /etc/hosts with a proper hostname. For simplicity I am using foreman.cloudalbania.com -> 192.168.0.180.
$ cat /etc/hosts
192.168.0.180 foreman.cloudalbania.com foreman
Reboot the server and make sure the new hostname is set.
$ hostname -f
foreman.cloudalbania.com
Install Katello & Foreman
Next step is to install the Foreman application with Katello content management.
This is a pretty straightforward step. First install the repositories
yum -y localinstall https://yum.theforeman.org/releases/1.24/el7/x86_64/foreman-release.rpm
yum -y localinstall https://fedorapeople.org/groups/katello/releases/yum/3.14/katello/el7/x86_64/katello-repos-latest.rpm
yum -y localinstall https://yum.puppet.com/puppet6-release-el-7.noarch.rpm
yum -y localinstall https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
yum -y install foreman-release-scl
Then update the OS and restart if any kernel or glibc upgrade
yum -y update
Install katello packages to prepare for the installation step later. This might take some time
yum -y install katello
Finally install foreman with katello. change the variables accordingly:
$ foreman-installer -v --scenario katello \
--foreman-initial-organization 'CloudAlbania' \
--foreman-initial-location 'YYZ' \
--foreman-initial-admin-username 'admin' \
--foreman-initial-admin-password 'password123' \
--foreman-foreman-url 'https://foreman.cloudalbania.com' \
After 10-15 minutes the server should be up and running and reachable from your browser
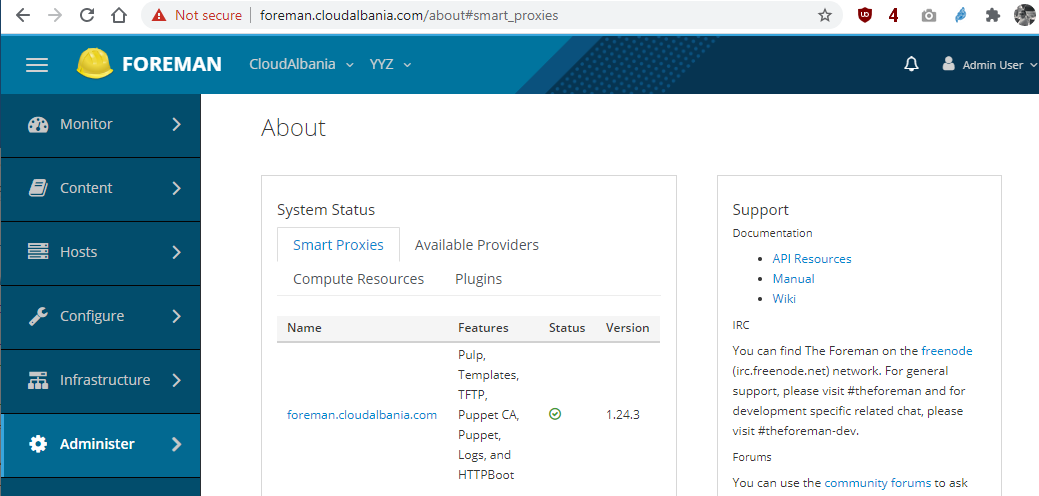
Install and configure the ansible server
To manage the Foreman server you can already do all the configurations in the GUI. If you need to have a more documented and automated configuration then Ansible is the way.
In this guide I am using a CentOS 7 server.
$ yum -y install epel-release
$ yum -y install ansible git
Make sure the ansible host can connect to the foreman server without a password the sake of this guide. You can implement vaults or sudo users in a production environment for better security
Create your ansible workplace:
$ mkdir -p git/foreman
$ cd git /foreman
Install the foreman.ansible collections:
$ ansible-galaxy collection install theforeman.foreman
Install the ansible dependencies with pip:
$ pip install subnet ipaddress rpm deb apypie PyYAML
Now your ansible server should be ready to configure the foreman server.
Using Foreman ansible collections
Full documentation for each individual module can be obtained with the ansible-doc command as follows:
ansible-doc theforeman.foreman.foreman_architecture
Managing Foreman - Your first playbook
In order to start configuring the Foreman server we can start with a Day 1 configuration item which is the Organization name.
NOTE: The Foreman collections do not need to connect to the foreman server itself rather we will use the local connection and then ansible will reach to foreman on port 443 (the API).
The first playbook we can start with is the definition of the Organization itself. Even though we have defined it in the setup command above, it is a good practice to have it defined in a configuration management system for consistency.
The playbook content:
[root@ansible foreman]# cat foreman1.yml
- name: Day 1
hosts: localhost
tasks:
- name: "Create CI Organization"
theforeman.foreman.organization:
username: "admin"
password: "password123"
server_url: "https://foreman.cloudalbania.com"
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
validate_certs: no
loop:
- "CloudAlbania"
- "Organization 2"
And when run we will see the below:
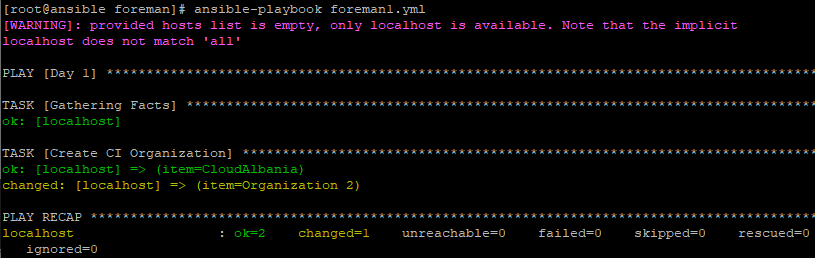
and in the foreman organizations list we will see:
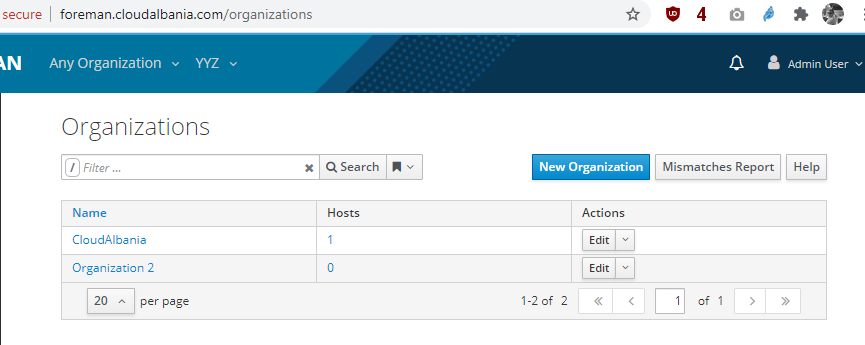
If we run again the playbook there will be no changes
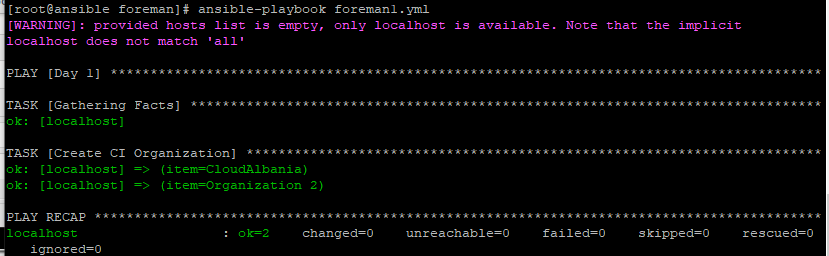
This is the end of this guide.
